The railway track of permanent nature which handles the normal commercial traffic regularly in called permanent way or permanent track.
A permanent way in railway is a combination of rails, sleepers, ballast fixtures, and fastening, etc. this is used to distinguish the finished and permanent track from a temporary track which is laid for temporary work L.e. for transporting construction material, earth, etc.
on the major construction sites. Such a temporary track is removed as soon as the construction work is completed.
The purpose or use of a permanent way is to provide permanent facilities for safe and quick movements of normal commercial traffic between the starting and destination station.

components of the permanent way in railway track
The followings are the components of the permanent way railway track:
- Formation of sub grade
- Ballast
- Sleepers
- Rails
- Fixtures and fastening
All these components parts of a permanent way are illustrated in Fig. 4.3
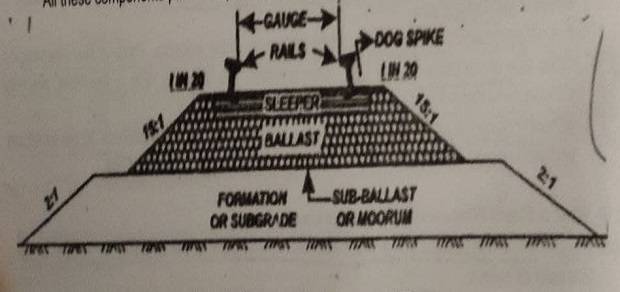
Requirement
- The gauge of the permanent way should be uniform, correct and it should not get altered.
- Both the rails should be at the same level on a tangent portion of the track
- The proper amount of superelevation should be provided to the outer rail above the inner rail on the curved portion of the track
- The permanent way should be sufficiently strong against lateral force
- The curves provided in the track should be properly designed
- An even and uniform gradient should be provided throughout the length of the track.
- The tractive resistance of the track should be minimum.
what do you mean by rail spikes What are their different types? Also, give the requirements of good spikes.
Spikes are used to fix rails to wooden sleepers. Types of Spikes
a) Dog spikes
b) Round spikes
c) Screw spikes
d) Elastic spikes
Dog spikes are the cheaper types of spikes which hold the rails at the correct gauge and can be easily fixed and removed.
These are commonly used for holding F.F rails. Four dog spikes are used per sleeper, two on either side of the rail.
The disadvantages of dog spikes are that these become loose under the wave action caused by the moving train.
Round spikes are used for fixing chairs of B.H rails to wooden sleepers and also for fixing slide chairs of points and crossing. These have either cylindrical or hemispherical heads or blunt ends.
Screw spikes are a tapered screws with V-threads. Their head is circular with a square projection and used to fasten rails with wooden sleepers. The holding power of these spikes is more than double to that of dog spikes and can resist the lateral thrust better than the dog spikes.
Elastic spikes are used for fixing F.F rails to wooden sleepers. These give better grip and result in a reduction of wear and tear of rail. The advantage if this type of spike is that it is not pulled up by the wave action of the moving train.
Requirements
- It should be easy in fixing or removing from the sleepers.
- It should hold the rails and bearing plates in the proper position.
- It should be cheap
- It should require minimum maintenance
- It should not come out of the sleepers under vibration
PERMANENT WAY IN CIVIL ENGINEERING || P-WAY || RAILS || GAUGE || SLEEPERS || BALLAST || FASTENER ||
Define fixtures and fastening in railways. What are their functions and types?
Fixtures and fastening in railways are fitting required for joining of rails end to end and also for fixing the rails to sleepers in a track.
Functions Fixtures and fastening in railways
g) To join the end of the rail to end to form the full length of track
h) To fix the rail to sleeper
i) To maintain the correct alignment of the track
j) To provide proper expansion gap between rails
k) To set the points and crossing in the proper position
l) To maintain the required tilt of rails
Types Fixtures and fastening in railways
a) Fish plates
b) Bearing plates
c) Spikes
d) Chairs
e) Bolts
f) Keys
g) Anticreepers
What is the effect of breaking the gauge? Discuss.
One country should have only one gauge throughout its various parts. But the policy of India and its topographical, geological, and financial conditions have led to adopt various gauges in its different parts. The various effects of breaking gauge or change of gauge are discussed below.-
Advantage
- The most effective advantage of breaking the gauge is to render the railway an economical and profitable concern
- It facilitates the provision of a steeper gradient sharp curves and narrow tunnels by adopting a less wide gauge in a hilly and rocky area
Disadvantage
- It causes much inconvenience to the passengers while changing the train at stations, with the change of gauge
- It causes a delay in the movement of people and goods
- It results in wastages of time
- It causes extreme difficulty in the quick movement of military and ammunition during war days.
what is ballast in railway engineering? What are the functions of blast?
The granular material spread on the formation of a railway track for the sleepers to erst upon to rest is known as ballast.
Functions of ballast in railway
1. To provide cushion effects to the track since it acts as an elastic medium in between the sleepers and the formation
2. To provide a firm bed for the sleepers to rest upon
3. To uniformly distributed a load of the train from the sleepers on a large area of the sub grade or formation
4. To hold the sleepers in their correct position and thus preventing their laterad and longitudinal movements
5. To provide an easy mans of maintaining the required levels of the two rails in a track on correcting track alignment.
6. To drain off the rain water from the track quickly and to provide a well-drained foundation bed immediately below the sleepers
7. To protect the top surface of the formation
8. To prevent the growth of weeds inside the track
Also, Check This