The member laid transversely under the rails for supporting and fixing them to the gauge distance apart are known as What is Sleepers.
Functions
- To support the rails firmly and evenly
- To hold the rails to the proper gauge
- To hold the rails at proper level or at an inwards transverse tilt
- To act as an elastic medium in between the rails and ballast and to counteract the tendency of wheels load to disturb the track
- To distribute the load coming on the rails over a sufficiently large area of the ballast
- To provide stability to the permanent way on the whole

Requirement
- The sleepers should be economical in their initial as well as maintenance costs.
- They should have a long life
- They should be able to maintain the correct gauge
- They should be quite durable i.e. they should be offered sufficient resistance to weathering agencies.
- They should be suitable to each type of ballast
- They should be suitable for track circuiting
- They should have such fitting that they can easily be removed replaced lifted and packed when required.
- They should have sufficient weight for their stability
- They should provide sufficient bearing area below the rail seat over the ballast
- They should be sufficiently strong to take bending stresses under the moving wheel loads
- They should be such a design that they are not damaged during packing and boxing of the ballast.
- They should be of such a design that they are not pushed out easily of their position in any direction even under maximum force of moving trains
- They should be able to resist impacts and vibration due to heavy wheel loads of speed trains.
- They should have a high scrap value.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of steel sleepers?
Advantages
- Steel sleepers manufactured in one piece
- These sleepers required few fastening which can be easily and quick manufactured
- These sleepers are light in weight and, therefore, can be easily handled
- The gauge can be adjusted and maintained by using steel slippers
- The lateral and longitudinal rigidity of the track laid with these sleepers is the best since the connection between steel sleepers and rails are strong
- Damage of steel sleepers is not too much during accidental or derailment
- The scrap value is more than wooden sleepers
- Creep can be efficiently checked by using these sleepers
Disadvantages
- Steel sleepers are costlier in their initial cost as compared to wooden sleepers
- These sleepers are liable to corrosion and hence cannot be used in station yards, industrial areas, coastal areas, and very wet or marshy areas.
- These sleepers are not suitable for every type of ballast
- Cracks are liable to develop at rail seats of these sleepers
- These sleepers are not suitable for track circuiting
- Renewal of track laid with steel sleepers is difficult.
What are sleepers# type of sleepers#use of sleepers in Indian railway
What is sleeper Density? On what factors it depends?
The number of sleepers used per rail length on a track is known as sleeper density of sleepers. The density of sleeper mainly depends upon the following factors:-
e) Axle-load which the track is expected to carry
f) Speed of the train.
g) Lateral thrust of locomotives
h) Methods of providing rails joints i.e. whether square or staggered. In the case of staggered joints, as on curves, extra sleepers are required because three or four sleepers on either side of each rail joint are placed closer together.
The number of sleepers, however, cannot be increased indefinitely, since a certain minimum space in between any two sleepers is required for packing ballast.
In India, this packing space is kept 30.5 cm to 35.5 cm. except at joints.
The number of sleepers per rail length varies in India from n+3 to n+6 for the main track, where n is the length of rail in meters.
In India, generally, the sleeper density of 18 sleepers per rails length is used. But the sleeper density on the mainline is being increased nowadays due to the increase in speed of the fast-moving train.
It is not necessary to keep uniformly spacing between all the sleepers.
Three or four sleepers, on either side of the rail joints, are kept closer together.
The sleepers, near to the joints, are very close to avoid loosening of ballast due to the impact of wheels loads.
In suspensions rail joints, the center distance between the shoulder sleeper is 30 cm to 45 cm, and that between the next sleepers, it is 75 cm to 90 cm, according to specifications.
What do you mean by tilting of rails? What are its objects Also discuss the advantages of it.
The art of placing the rails of a track at an inwards slope of the train is called tilting of rails. In case, the rails of a track are placed in a vertical position, the top surface will not come in full contact with the treads of wheels of a train due to coning of wheels and the pressure of wheels will always be exerted near the inner edges of the rails. Therefore, the rails will wear out quickly.
make full contact of the top surface and thereby reducing the wear of rails in this way, these are placed at an inwards slope of 1 in 20, which is known as tilting of raids.
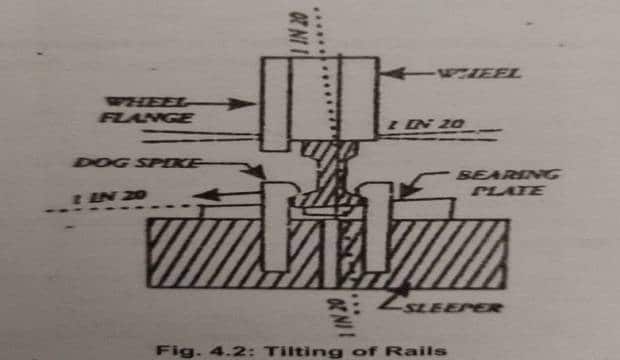
The main objective of tilting of rails is to reduce the wear on the inside edges of rails in a track.
The required tilt is provided at rail seats in bearing plates, chairs, and metal sleepers at the firm of their rolling or casting.
The wooden sleepers, which are used without bearing plates, are adzed to a required tilt of 1 in 20 at the rail seats.
Advantages
- The gauge can be properly maintained by tilting of rails
- The wear of the railhead is uniform due to the tilting of rails
- The life if rails are sleepers increases due to tilting of rails.
What is creep? How the creep is measured?
The longitudinal movements of rails in a track are known as travel or creep of rails. It occurs in almost all railways track but varies in magnitude considerably. In some locations, the creep may be several centimeters in a month, while in other locations, it may be negligible in that Period.
Measurement of Creep
Creep is measured by using a creep indicator which is described below:-
Alter laying the track, two small posts of rails are embedded on both sides of the track in such a manner that the line joining the center of these two rails posts in perpendicular to the centerline of the track.
Their top-level is kept n level with the top surface as illustrated. Chisel marks are made on the posts and a thin string is stretched between them.
Marks are also made by chisel where the string touches the bottom flanges of rails.
when the creep is to be measured,.a.string is stretched in between the marks made on the posts Thus the distance between the strings and the mark made on the bottom flanges of the two railed indicates the creep of rails at that place.
Also, Check This