Types of road work procedure, light, drainage, and water are the basics in the development of any land. In building construction, roads are constructed for large projects.
When developing land for a township or for a number of buildings, proper planning, and execution of internal roads become the salient features of the project.
The clients insist on the construction of quality road work procedures ways as a permanent structure of the project.
An engineer working on the building project should not neglect the importance of this activity.
He should be aware of the specifications, execution procedures, and maintenance of the road.
In this chapter, we will discuss the planning, designing, and construction of internal types of road work procedures, with checklists to maintain quality work.
|
|
PRELIMINARY REQUIREMENTS BEFORE ROAD WORK PROCEDURE EXECUTION
1. DRAWINGS
- Contour survey plan of the complete plot.
- Trial pit section, showing variation and thickness of strata.
- Approved layout for roads.
- Categories of road, with width and type of road.
- Complete ‘L’ section of all internal roads to work out the quantities of excavation and filling.
- Details of a system for surface drain off.
- Slopes and turning radius at various points.
2. AVAILABILITY OF MATERIAL AND LABOUR
- This survey helps in preparing a bar chart of the work.
- It helps in preparing the material and labour schedules.
- The machinery involved are costly and is usually rented. A detailed survey and planning help in the optimum use of this machinery.
3. PERMISSION OF AUTHORITIES CONCERNED (IF REQUIRED)
- Excavation in the rock by blasting.
- Demolition of any existing structure.
- Cutting of existing trees.
- Crossing or diverting of nalla or drainage works.
Road Inspection Checklist Free Pdf Download Link Below
TOOLS AND MACHINERIES REQUIRED FOR THE ROAD WORK PROCEDURE
Different types of tools and machineries are used for various types of roads as listed below.
- Tools
- Ghamela, phavda, tikaw, crowbar, etc.
- Bull doser, tractor, rooter, lwed scraper, shovel units with trucks.
- Bitumen boilers, sprayer, aggregate spreader, bitumen mix spreading machine, grouting machine, bitumen pavera.
- Conerete mixer, Conerete pavere, concrete.
- vibrators, float, templates, etc.
TYPES OF ROAD
- W.B.M. (Water Dound Macadam)
- BITUMINOUS ROADS
- CONCRETE ROADS – TRIMIX
The cross-section of any roadshows the following layers
FORMATION (Excavation and murum filling)
This is the final ground surface, after the completion of earthwork. It is the foundation to which traffic load is directly transmitted. It is natural soil or excavated strata if the road is in cutting. It may be the top surface of the finally shaped embankment earth, during road filing.
BASE COURSE (Soling)
It is the first layer of the road structure laid over the soil formation. The main purpose of this layer is to spread the traffic load, sufficiently, to prevent overstressing of the formation. This is achieved by providing soling. Soling is done with hand-packed big stones called rubble.
BASE COAT (Metalling)
It is the Intermediate course between the base course and the wearing coat. It is made of well-consolidated stone aggregates. This course is meant for the stability of the road under traffic and resistance. The resistance against wearing varies with the thickness of this layer.
WEARING COAT
It is the topmost coat of the road, over which the traffic moves. The wearing coat reduces the harmful effects of the climate, protects the road from rain, and provides a smooth riding surface for traffic. The wearing coat material varies as per the requirement.
1. WATER BOUND MACADAM ROAD (W.B.M.)
This is the cheapest and the most widely used of temporary roads. For small colonies and low-budget schemes, this type of road is preferable. The aggregate used for its construction is known as macadam.
MATERIAL REQUIRED FOR W.B.M. ROAD
Murum, gravel, rubble (230mm), stone chips, metal (40 to 50mm), water, etc.
WORK PROCEDURE FOR W.B.M. ROAD
FORMATION
- Excavate the trench for the width is given in the drawing.
- While excavating keep “Deadman’s” (Tale tells) in a staggered manner, to find out the average depth of excavation. It also helps to classify the excavated strata.
- Fill the murum in line, level, and grade up to formation level including rolling by 8 to 10 T roller.

SOLING
- Provide and lay the soling 230mm in height. hand-packed and firmly bedded in position to minimize the voids.
- Fill the voids with small stone pieces and roll the surface with a10 T roller.
METALLING
- Spread metalling of 40 to 50mm size in one or two layers, each layer is 12cm. Fill the gaps with smaller pieces.
- Confirm the surface to the required camber and gradient.
- Camber provided is generally 1 in 30 to 1 in 40 while the gradient is 1 in 100 (minimum).
- Dry rolling with a suitable roller should be done beginning with the edges to compact the layer from 12cm to 7.5cm.
- Ensure proper rolling of each layer.
- Spread soft murum or stone screening as a binding layer of 20 to 25mm thickness.
- Sprinkle water over the surface and roll it, to get the required top surface.
- After drying. open the road for traffic.
CHECKLIST FOR W.B.M. ROAD.
- Strata checking by a trial pit.
- Bearing capacity of the soil.
- Formation level and surface after dry and wet rolling.
- Checking all drawings before execution.
- Size and grading of the coarse aggregate.
- Quality of the binding material.
- Line, level, gradients, camber, and superelevation of the road, periodically at each layer.
- The thickness of each layer after rolling.
2. BITUMINOUS ROADS
- semi grout bituminous road.
- full grout bituminous road.
MATERIAL REQUIRED AND IT’S SPECIFICATIONS
- Murum
- Gravel
- Rubble
- Stone chips
- Metal from 15mm to 40mm
- Grit, stone dust
- Bitumen 80/100
SPECIFICATION OF BITUMEN
- The grade or quality of bitumen is confirmed by its penetration test. The lower the penetration, the harder is the bitumen.
- The bitumen for roads is available in the range of 30/40, 60/7o, 80/100, etc. Normally. 80/100 bitumen is recommended and used for semi and full-grout roads.
- 80/100 denotes the distance in mm that the penetrated vertically by the standard needle in the sample at 25° c in 5 seconds, with a 100gm load (penetration may vary from 80mm to 100mm).
- Hot bitumen (melted) is used for the construction of roads. The applied temperature varies from 177°c to 191°c.
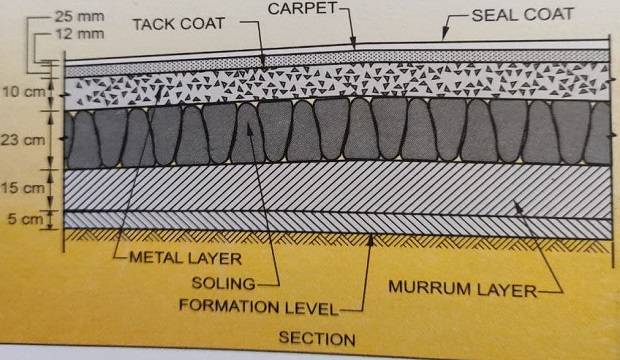
WORK PROCEDURE FOR BITUMINOUS ROADS
EXCAVATION
Excavate the areas for the width as detailed in the drawings.
CHECKING LINE, LEVEL, AND SLOPE
Ensure that the surface is in the proper line, level, slope, camber, superelevation, curves, etc.
MURUM LAYING
Provide and lay the murum in two layers. Each layer should be watered and then compacted with a roller to a thickness of 15cm. A Roller of 10 T capacity should be used for compaction.
SOLING
Provide hand-packed soling at the edge of 23cm height. Fill the chips in voids and roll with 10 – 12 T roller.
METALLING
The hand-broken metal of size 50mm (2″) should be laid on the surface. The thickness of the metalling should be 10cm compacted to 7.5cm thick with 10 to 12 T roller.
GROUTING
- After satisfactory compaction, check the gradient’s slopes. Grouting should be done by bitumen, at the rate of 2.7 kg/sq.m. to penetrate to a depth of 2 to 2.5cm below the surface of the metal for semi-grout.
- For full grouting, approximately 8 to 10kg/ sq.m. bitumen should be used to penetrate to a depth of 5 to 7.5cm below the surface of the metal.
- During grouting spread the stone grit over the grouted surface. Ensure proper rolling by a road roller.
TACK COAT
Clean the grouted surface with a wire brush. Apply the tack coat of bitumen @ 1.5 kg/ sq.m.
CARPET
- Prepare bituminous macadam by mixing.
- 20mm to 12mm metal in 2:1 proportion.
- Ensure that every metal is covered with bitumen at the rate of 86kg/100sq.m.
- Spread this layer immediately for a thickness of 40mm, to be compacted by rolling to a level thickness of 25mm.
- If specified and required, clean this bituminous macadam and apply a tack coat.
SEAL COAT
10 to 12mm seal coat (with 95kg of metal to 5kg of tar) is applied and rolled with 10 to 12 T roller.
Open the road to traffic.
CHECKLIST FOR BITUMINOUS ROAD WORK PROCEDURE
- Check the formation level, and excavated level. width of excavation etc.
- Check the compaction of the formation level, as all the load is to be transmitted to this foundation.
- Confirm the compaction by measuring passes of the road roller or by density test.
- Check the quality of bitumen for penetration.
- Visualize its resistance to the flow.
- Check and confirm the consumption of bitumen, as per specifications by taking the actual weight of bitumen containers before and after the application in a specified area.
- For larger areas, insist on a boozer to spray the bitumen, for uniformity and for maintaining the temperature.
- Check the bituminous macadam for uniform mixing. Check the thickness and uniformity of the bituminous macadam.
PRACTICAL TEST FOR COMPACTION OF MURUM FILLING
- Take a bore in a compacted layer by the rod.
- Remove the loose material and weigh it (W1).
- Pour the pre-weighed fine sand slowly in this bore until it is full.
- Measure the balance sand and find out the weight of poured sand (W2).
- If W2 and W1 tally without any major variation, then the surface is said to be well compacted.
3. CONCRETE ROADS
Since roads play an important role in the development of any land, always maintain a smooth and good appearance of the roads. Concrete roads are therefore constructed, although they are expensive as compared to the other two. types of roads discussed earlier.
Concrete roads are of two types. Plane concrete and reinforced concrete roads. However, plain concrete roads are widely used. They are discussed below.

4. TRIMIX CONCRETE WORK FOR ROAD
- Here is an extra amount of water present in the concrete that is extracted to minimize the water-cement ration.
- This is down with a vacuum pump.
- After placing concrete the filter sheet is spread on the concrete road and extra water present on the sheet is extracted by a vacuum pump.

REQUIREMENTS AND ROAD SIGNS
STORMWATER DRAINS
- The camber and slopes of the road should ensure that water does not stagnate on the road.
- The water flowing from the road is first collected inside the drains, which in turn are let into the cross drains, as shown in the figure. Catch water drain is provided to collect water, either pumped out or let into the main road stormwater drain.
- The cross drains are covered with removable grit covers, which may be of concrete or C.I.

CONDUCTING OF SERVICES
Various service lines such as electrical, telephone, drainage, etc. have to pass across the types of road work procedure. Planning and drawing of these línes should be passed through G.I./hume pipes, laid below the road, before execution.
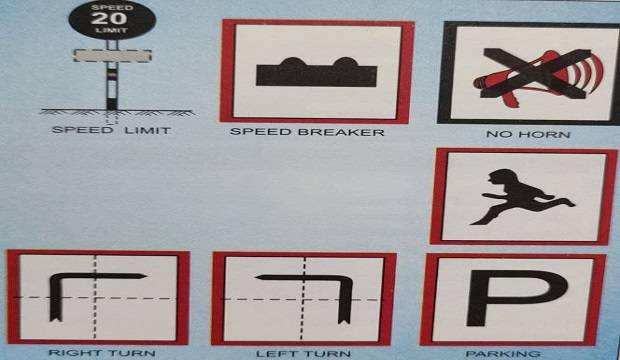
ROAD SIGNS
- Place road signs for safe traffic in the premises.
- Provide speed breakers near the junction of roads.
- Provide guard stones and divider markings with white paint, wherever necessary.
- Provide block-wise/building-wise boards to turn and bypass roads.
- Provide islands for smooth traffic in squares.
- Do not mark parking areas on the road.
- Plan and maintain roadside plantations.
- Provide street 1ights at regular intervals.
- Clean the wearing coat daily and attend to minor repairs periodically.
Also, Read This.
