8 Types Of Piles Foundation Used In Construction
1. Cast-In-Place Concrete Piles
2. Precast Concrete Piles
3. Steel Piles
4. Timber Piles
5. Cast in place concrete
6. Precast concrete piles
7. Steel piles
8. Timbe
a. CAST IN PLACE CONCRETE PILES
1. Formed by driving a cylindrical steel shell into the ground to the desired depth and cavity of shell is filled with fluid concrete.
2. The steel shell doesn’t contribute to the load transfer capacity of the pile.
3. It’s purpose is to open a hole in a ground and keep it open to facilitate the construction of concrete pile. (same function as formwork)
4. Vigilant quality control & good construction practice are necessary to ensure the integrity of cast-in-place piles.
b. PRECAST CONCRETE PILES
1. Usually have square/circular/octagonal cross sections.
2. Fabricated in a construction yard from reinforced or pre-stressed concrete.
3. Disadvantages of this pile are problems in transporting long piles, cutting and lengthening.
4. It has higher capacity than timber piles.
c. STEEL PILES
1. It comes in various shapes & sizes
2. Steel H-Piles are rolled steel sections
3. Steel pipe piles are seamless pipes that can be welded to yield lengths up to 70m.
4. They are usually driven with open ends into the soil.
5. A conical tip is used where the piles have to penetrate boulders & rocks.
6. However it needs to be treated before embedded in corrosive environment.
d. TIMBER PILES
1. Have been used since ancient times
2. Length of timber piles depends on types of trees used to harvest the piles,
3. Common length are 12m
4. It is susceptible to termites, marine organisms and rot within zones exposed to seasonal changes.
5. Even though it’s cheaper but it has low capacity and can’t take hard driving.
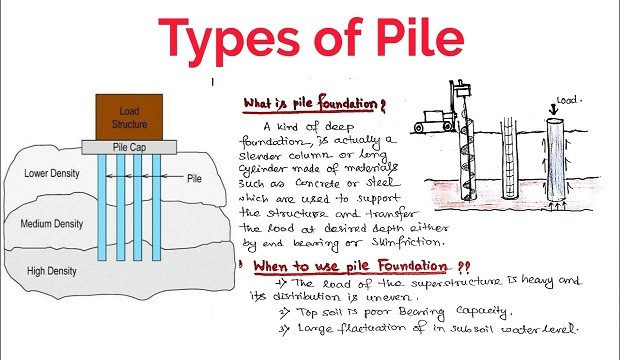
Types of Pile Foundation
Different types of load bearing piles?
Following are the Types of load bearing piles:
a. End bearing piles
b. Friction plies
c. Timber piles
d. Fill piles or piles in fill
a. End bearing piles are those, which terminate in hard, relatively impenetrable material such as rock or very dense sand and gravel. They dorive most of their carrying capacity from the resistance of the stratum at the toe of the pile.
b. Friction piles
Friction piles obtain a greater part of their carrying capacity by skin friction or adhesion.
This tends to occur when piles do not reach an impenetrable stratum but are driven for some distance into a penetrable soil.
Their carrying capacity is derived partly from and bearing and partly from skin friction between the embedded surface of the soil and the surrounding soil.
c. Timber piles
The piles made of wood are called timber piles. The timber used for their construction should be free from the defects, decay etc. and it should be well seasoned.
These piles are circular (200mm to 500mm in diameter) or square (150mm to 500mm side) in crosssection. Length of these piles is generally 20 times their sides or diameter.
d. Piles in fill
Piles that pass through layers of moderately- to poorly-compacted fill will be affected by negative skin friction, which produces a downward drag along the pile shaft and therefore an additional load on the pile. This occurs as the fill consolidates under its own weight.
List the factors influencing the choice of pile to be constructed for a particular foundation?
Following are the factors influencing choice of pile to be constructed for a particular foundation:
- Location and type of structure
- Ground conditions
- Durability
- Cost
There are many factors that can affect the choice of a piled foundation. All factors need to be considered and their relative importance taken into account before reaching a final decision.
Location and type of structure For structures over water, such as wharves and Jettles, driven piles or driven cast-in-place plles (in which the shell remains in place) are the most suitable.
On land the choice not so straight forward. Driven cast-in-place types are usually the cheapest for moderate loadings. However, it is often necessary for piles to be installed without causing any significant ground heave or vibrations because of their proximity to existing structures.
In such cases, the bored cast-in-place pile is the most suitable.
For heavy structures exerting large foundation loads, large-diameter bored piles are usually the most economical.
Jacked piles are suitable for underpinning existing structures.
Ground conditions Driven piles cannot be used economically in ground containing boulders, or in clays when ground heave would be detrimental.
Similarly, bored piles would not be suitable in loose water-bearing sand, and under-reamed bases cannot be used in cohesion less soils since they are susceptible to collapse before the concrete can be placed.
Durability This tends to affect the choice of material. For example, concrete piles are usually used in marine conditions since steel piles are susceptible to corrosion in such conditions and timber piles can be attacked by boring molluscs.
However, on land, concrete piles are not always the best choice, especially where the soil contains sulphates or other harmful substances.
Cost In coming to the final decision over the choice of pile, cost has considerable Importance.
The overall cost of installing piles includes the actual cost of the material, the time required for piling in the construction plan, test loading, the cost of the engineer to oversee Installation and loading, and the cost of organization and overheads incurred between proceed.
The time of initial site clearance and the time when construction of the superstructure can proceed.
Also, Read This