The maintenance bituminous roads consist of:
1. Patch repairing work: It is carried out when localized pot holes are developed on the surface of the road. Repairing of pot holes are carried out in the following stages:
2. Cutting of pot holes : The pot holes are marked on the road surface. Cutting of marker areas is done in rectangular shape and all the affected material are then removed from
3. Cleaning of pot holes : The cut pot holes are cleaned of all loose material and dust A prime coat of bituminous binder is then applied in the pot holes.
4. Preparing Premix: Coarse aggregates and bitumen are mixed in desired proportion to get a premix. I heating facilities are not available, premix is prepared by cold process using emulsion or cutbacks. While preparing premix it should ensure that the prepared premix is similar in composition of the original construction.
5. Filling the Premix: The premix is filled in the prepared pot holes and is compacted by using rammer.
When the pot holes is more than 75mm deep, the filling should be done in two or three layers and each layer is rammed before placing the next layer.
The finished surface of pot hole should be kept slightly higher than the original level to allow further compaction.

Surface treatment: Bituminous pavement becomes slippery and patchy due to bleeding of excess bitumen, used during construction, in the surface coarse. Defects like rutting, shoving or corrugations developed in such pavement surface.
such as trouble can be rectified by spreading blotting materials like aggregate chips of a maximum 10mm size of coarse sand.
Rolling is also done to develop a permanent bond between the existing surface and new material.
The binders in the bituminous surfaces also get oxidized due to ageing and develop minute cracks in the pavement surfaces.
Such surfaces can be rectified by applying a renewal coat or seal coat.
If the damage to the surface, due to oxidation or volatilization of binders is considerable, more than one layer of surface treatment may be applied.
Resurfacing: When the pavement surface is totally worn out and developed a poor riding surface, laying of an additional surface course on the existing surface may be more economical.
Resurfacing operation consists of cleaning the road surface, applying seal coat, aggregate chips, and rolling.
What type of maintenance cement concrete roads. Explain in detail?
Cement concrete roads need very little of maintenance if they are properly designed and constructed.
In this type of road, the main defect is the formation of cracks. The cracks developed in the road should be seriously examined and causes are ascertained before any remedial measures are suggested.
Treatment of Cracks
The common defect noticed in a cement concrete road slab is the appearance of cracks.
Cracks can be structural cracks, contraction cracks, shrinkage cracks, warping cracks, and corner cracks. The cracks are of varying width.
Fine cracks or hair cracks are not harmful and do not need Immediate maintenance.
Medium and wide cracks are harmful as they can cause progressive destruction of the subgrade by allowing water to per locate.
These cracks are first cleaned by removing dirt, sand, and loose particles using a stiff brush, a sharp tool or by a pressure blower.
Kerosene oil is applied on the cleaned cracks for proper bonding of sealing material.
Cracks are then filled with liquid bituminous materials like bituminous emulsion, cut back or joint sealing compound, whose basic ingredient is a bitumen.
This sealing material is placed up to 3 mm above the level of the road slab along the cracks.
A layer of sand is then spread over it to prevent the removal of the sealer under traffic.
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR OF ROADS|Maintenance of bituminous road and cement concrete roads
Maintenance of joints
The weakest part of cement concrete pavement is the joint. Most of the failure in the cement-concrete pavement is observed at or near the joints.
Therefore, periodic inspection is to be done to see that the filler and sealer material used in the joints are intact.
During summer the sealer material is squeezed out of the joint due to the expansion of CC slab.
The open-up joints are cleaned properly and refilled with joint sealer material.
After several years of pavement life, the joint filler material at expansion joints may get damaged.
These damaged or deteriorated filler and sealer materials are removed from the joint.
The top joints are then cleaned and fresh filler material is placed. The top is then sealed with sealer material. The best time to do this type of maintenance is the winter season.
Give the Advantage and Disadvantages of Rigid Pavements.
Advantage:
- It provides a good riding surface
- The life of cement concrete pavement is more
- Maintenance cost is low
- The vehicle operation cost is minimum
- Tractive or rolling resistance is low
- It provides high nighttime visibility
Disadvantage:
- The initial cost of construction is very high
- It requires skilled persons for constructions
- Constructions time required is more
- It takes more time for opening to traffic after construction
- Underground cables and sewers cannot be laid after constriction of the pavement
- Concrete pavement produces a noise when used by horse-drawn vehicles
What are the specification of materials required for the construction of cement concrete pavement?
Cement, coarse aggregates, fine aggregates, and water are required for the construction of plains cement concrete slabs. In the case of reinforced cement concrete slabs, steels wire fabrics or bars mats are used as reinforcement.
The cement used for most of the works is órdinary portal cement conforming to all tests as per IS 269.
Rapid hardening cement is also used to reduce curing time in case of urgency.
Now a day’s Portland blast furnace slag cement is more preferred than ordinary portend cement.
Coarse aggregates used are crushed stone or gravel confirming all tests as per IS 383.
The aggregates should be clean, hard, and free from harmful materials like iron, cola, mica, clay, etc. The physical requirements of coarse aggregates are given in the table.
The grading for coarse aggregates is given in the table.
What are the various types of failures in the flexible pavement? Explain the cause.
Failures: The localized deformation or settlement of anyone off the layers of flexible pavement leads to the entire pavement. The failure of flexible pavement may be due to
a) Sub. grade-failure
b) Base Course. failure or
c) Wearing course failure
Sub-Grade Failure: Excessive deformation in sub-grade soil is one of the main causes of pavement failure.
This type of failure causes excessive undulation or waves and corrugations in the pavement’s surface.
The basic reasons of subgrade failure are:
- Inadequate stability due to improper compaction or presence of excessive moisture in the soil
- Excessive stress in the soil
- Inadequate road drainage

Base Course Failure: The following are the main type of base course failure:
- Inadequate stability
- Loss f binding action
- Crushing of base course material
- Lack of lateral confinement of base course
- Inadequate road drainage
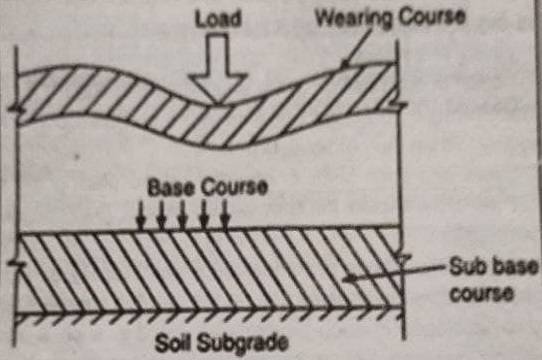
Wearing Course Failure: The failure in wearing course is mainly due to the following reasons:
- Lack of proper mix design of inadequate quantity of binder
- Use of inferior quality of the binder
- Inadequate quality control
- Volatilization and oxidation of binder.

Also, Check This.