The total construction cost, almost 65% is the material cost that can go up due to negligence by the engineer organization.

ACTIVITIES INVOLVED IN-STORE KEEPING AND MATERIAL STACKING AT CONSTRUCTION SITE
- Materials inward recording.
- Materials issue recording.
- Materials consumption & reconciliation.
- Materials safety and stacking.
- Stock checking,
- Updating of materials stock.
- Control on the wastage of materials.
- Control on quantity and quality of materials.
- Reporting to H.O. for bill settlements.
STORE RECORDS: OBSERVE THE FOLLOWING
- Recording of details to be done in-stock books. registers, notebooks, etc. by the storekeeper.
- The storekeeper should use the prescribed format for recording. All materials received must be recorded daily in this book. The sequence of materials and their heads will remain the same for all the sites of the organization.
- All materials issued will be recorded in two separate registers, as consumable items and non-consumable items. consumption entry will be made in the stock book as per the records of this register.
- Physical balance stock checking and certification on the stock book by project heads will be done on the 15th and 30th of each periodical month.
- All entries should be recorded in a neat and legible manner.
- Continuation of records from one stock book to another book etc. should be clearly mentioned.
- The different types of recordings and entries are given in detail below.
1. STOCK BOOK
Stock books should be maintained in the order SB 1. SB-2. SB-3 etc.
SB-1: STATIONERY
It shows the stock of all stationery, format, reports, notebooks, stock books, etc.
SB-2: BUILDING MATERIALS
It shows the stock of bricks blocks, binding wire, brickbat, cement, chemicals, dust, rubble, empty bags, grit, lime, metal, murum, sand, sanla, steel shingle, tiles. waterproofing powder, white cement, etc.
SB-3: DOORS WINDOWS FRAMES SHUTTERS ETC.
It shows the stock of door frames (wooden/MS), door shutters, door fittings, cover mouldings, lapping Patti M.S. windows, Aluminium windows, rolling shutters, collapsible shutters, main gate, side gate, trap doors, R.C.C. grills, glass panes, etc.
SB-4: GI. MATERIALS
It shows the stock of all G.l. pipes and fittings, hobak holdtite, kiltan, tar, tag, etc.
SB-5: C.I., C.P. AND SANITARY MATERIALS
It shows the stocks of pipes, fittings, chamber covers A.C. material pipes, and fittings. All sanitary wares W.H.B., soap dish, W.C. pans, all plumbing C.P fitting, etc.
SB-6: P.V.C, AND R.C.C, PIPES, AND FITTINGS
It shows the stock of.
P.V.C. Materials
Pipes and fittings, solvents, clamps, etc.
R.C.C. Hume Pipe
Pipes, coolers, chamber covers, packing rope, etc.
SB-7: ELECTRICAL MATERIALS
It shows the stock of all electrical materials, purchased for electrification and maintenance (excluding contractor’s material).
SB-8: GENERAL MATERIALS
The supervisor should enter the presentee of the daily departmental labour, appointed for various works in this register. Cash bills prepared every week will be based on this register and should be checked by the site engineer.
WATCHMAN’S CHARGE REGISTER
- This register can be maintained for the material lying outside the godowns.
- Charge of such material should be given to the watchman by the storekeeper during night- hours.
- The storekeeper should enter the details of locking arrangements for various stores, godowns steelyard, etc. in this register.
- Details of material lying in the parking/open spaces should be indicated in this register along with their quantities.
- The storekeeper should ask the security guards to sign on this register in the evening while handing over the charge in night. He should resume the charge in the morning before the work begins.
- (on the site outside the site)
- All shifting of excavated earth, murum rubble, debris, etc, should be recorded in this register.
- All material shifting whether on the site itself or. to any locations outside must be recorded by the storekeeper.
CEMENT ISSUE REGISTER
- The issuing of cement should be recorded daily by the storekeeper. He should record the number of cement bags issued as per the issue slip and also bags returned if any indicating the actual consumption.
- These consumption records should be used at the end of the day to prepare D.P.R.
- Here, consumable items are recorded in the order issued by the storekeeper on a daily basis.
- These entries must be followed by the signatures of the persons to whom the material was issued.
NON-CONSUMABLE ITEM ISSUE REGISTER
- This register records the issue and the return of materials like tools, equipment, ghamela, tikav, phavada, electrical wires, floodlights, lighting arrangements, drilling machines, scaffolding material, M.S. ghodi, hose-pipe. pumps, mixer, vibrator, lift, etc.
- All materials/ machinery/equipment should be issued as per the instruction of the site in-charge.
- While accepting the material back the from user, it should be checked and damages, if any should be recorded. Damages should be treated with strict action by the store keeper with help from the site in-charge. Memo notes should be raised accordingly.
BLOCK MAKING REGISTER
- All the information regarding block manufacturing should be recorded by the storekeeper on a daily basis.
- It should show the number of blocks manufactured, the number of cement bags consumed, the number of blocks used for a particular day for different sizes.
- Based on this, cash bills for labour payment of block-making work can be prepared.
3. NOTEBOOKS
CASH PURCHASE NOTEBOOK
For entering the details of all cash purchases done at the site along with the entries of the bill, challan. amount etc.
WATCHMAN’S NOTEBOOK FOR MATERIAL ENTRY
To record all the entry and exit details of materials supplied at the site, along with the supplier’s name, quantity, timings, etc. This entry is made on the watchman’s report at the end of the day. It should be compared with the records and challans available with the store keeping and material stacking at construction site.
KEY NOTEBOOK
This will record the details of all the locks used on the site along with their key number and the person in charge of the key.
4. DISPLAY RECORDS IN STORES
UPDATED RECEIPT OF BUILDING MATERIALS
- This chart displays the cumulative receipt of all building materials, serially written, and the quantity used per day for 31 days.
- (For example Steel, Cement, Sand, Bricks, Metal, Blocks, etc.)
- This chart will help update the consumption and total receipt of materials.
REGARDING MINOR WASTAGE
- Minor wastage will be recorded by the storekeeper in accordance with the instructions of the engineer.
- The acceptance signature of the concerned person is also required. A memo note should be raised against any such entries and necessary action should be taken with help from the site in charge.
- For example, 1/2 bag cement wastage, mortar wastage, bricks are broken, sand mixed with debris, etc.
UPDATED STOCK MATERIALS RECORDINGS ON SLATES
- Materials like cement, plumbing fittings. carpentry fittings etc. should display small slates to indicate the stock in cement godowns and plumbing material racks.
- This will indicate the balance stock of material on a particular day.
- It will also help in finding out the immediate status of the stock at any given time and the minimum stock level of each material while placing a new requirement.
PROCEDURE FOR RECEIVING AND RECORDING OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AT SITE
Delivery challans, while receiving any material, should specify the time and the receipt date. They should also carry the stamp of the site with the watchman’s signature.
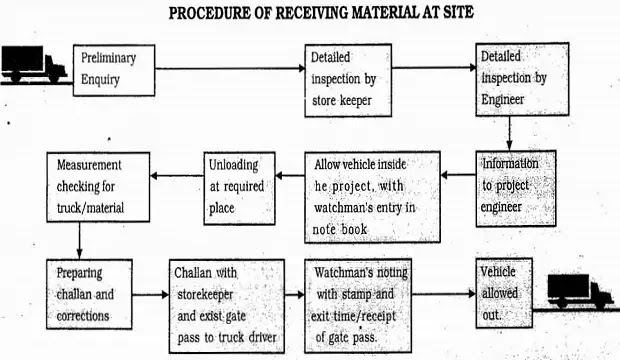 |
PROCEDURE FOR RECEIVING MATERIAL AT SITE AND RECORDING OF MATERIALS |
This procedure is described in the chart.
While receiving material, the following steps will help avoid any mistakes in recording, quantity checking, and quality checking.
STEP 1
- The security personnel should complete the preliminary inquiries when material transport like tempo/truck/auto arrives at the entrance gate.
- The material should then be checked for quantity, measurement of material. type. quality, make, damages, defects, duplication, etc. and any anomalies should be mentioned on challan.
- If the quality does not match the specifications, the material should be rejected without unloading it (truckload) on site.
- If any material, other than the building material, differs from the specifications on the challan. it should be noted on the delivery challan The supplier should also be informed of it.
- The material should be unloaded to avoid any hindrance to activities like stock checking/issuing of material.
- If required, site engineers should help in stacking the material at the proper place.
- The storekeeper should inform the respective site engineer and project engineer after receiving the material.
- The project address on the challan should be checked. Any doubts about quantity should be communicated to the storekeeper.
STEP 2
- The storekeeper should check the documents, confirm the validity of the supply with the engineer, and decide on the location for unloading.
- A sample checking for quality should be done at this stage with help from the engineer.
STEP 3
If the engineer cannot verily the supply/quality, he should inform the project engineer of the details regarding the supply/quantity of material.
STEP 4
After confirming that the material is required at the site and the supply is being done through proper channels, permission is given for the vehicle to enter.
STEP 5
- The watchman will note down the entry time and the details regarding the supplier, material quantity, etc. in his notebook.
- Unloading will be done at the location (e.g near working place/inside material godown/near store) indicated by the storekeeper.
STEP 6
- The storekeeper will supervise the unloading operation.
- If the material is found to be defective or of bad quality, after unloading, it will be referred to as the concerned driver.
- Measurements of truck/material will be taken in the presence of the driver.
- The driver will be informed of any comments to be written on the challan and his consent signature will be taken on both copies.
- Complete information about the material, quantity received, disparities of measurement, material to be returned, etc. should be noted clearly on the challan. The storekeeper should seal it with the project stamp and his signature.
- He should also prepare the gate pass in duplicate.
- The gate pass is the permission for the truck to leave the site premises. Details of any material going out should be mentioned on the gate pass along with the exit time.
STEP 7
The watchman should sign and stamp the duplicate challan copy. He should also check the gate pass for the contents in the outgoing vehicle. Only then the vehicle is permitted to go out.
NOTE
In case the material is to be rejected, the storekeeper informs the project in charge of it. He, in turn, will intimate the purchasing department, and a decision to be reached after discussions.
BUILDING CONSTRUCTION MATERIAL STACKING AND PRECAUTIONS
- The storekeeper should take precautions while stacking all materials. General norms followed are listed below –
- The site engineer should be informed immediately of the receipt of materials, to finalize the stacking location.
- The material should be stacked nearest to their immediate required place.
- It should be stacked so that the material received first, is utilized first.
- All materials should be stacked in locked godowns. In case this is not possible, then at least M.S. chains should be tied for securing the items kept in open spaces/parking, etc.
- The security guards should be informed of any such items to ensure that daily counting and checking are observed.
- Fragile and expensive items like plumbing fittings and sanitary ware should be utilized immediately. The stacking period should be minimum. Unnecessary handling should be avoided.
- Since building materials get affected by water, necessary precautions should be taken to avoid dampness at places of storage.
- Up-to-date records of the stock must be maintained on a daily basis. A minimum level of stock should be maintained for each item and should be stacked at convenient locations.
- In case Interoffice Correspondence (I.O.C.) is received for the transfer of material to other sites, it should be easily located.
- The storekeeper should also check the collection/ accumulation of scrap material periodically. It should be stacked properly.
- The project in-charge should inform the purchasing department to arrange for the disposal of this scrap (e.g. empty cement bags, steel scrap, etc.).
I.O.C. OF MATERIAL RECEIPT TRANSFER TO OTHER SITES
- The storekeeper should exercise caution while handling an I.O.C. When the purchase department issues an I.O.C. for collection of material from the site, a Jr. Engineer Supervisor from other sites approaches with the I.O.C. to collect the material. In this situation, the following precautions should be taken.
- All transfers of material should be assigned to a Junior Engineer/Supervisor. Labour should not be deputed for these transactions.
- The storekeeper should check the quantities and specifications of the materials to be issued. The person accepting the material should also check all the details in the I.O.C.
- If the material referred to in the I.O.C. is not available on-site, the purchase department should be informed of the details of consumption of the material and hence the non-availability of the same.
- After the transfer as per the I.O.C., consumption entries of the material should be entered immediately and the records should be updated by the storekeeper.
STORING STACKING OF IMPORTANT CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS
1. CEMENT
- Cement should be stored on a raised platform, about 15 cm (6″) above ground level.
- Flooring should be damp-proof.
- Ventilators should be as minimum as possible in Size and number.
- Water should not seep in the store through doors/ windows.
- To avoid loss in strength due to storage, the first-in-first-out (old stock/new stock) system should be followed.
- A maximum of 10 bags should be stored in each stack.
- The receipt date of cement should be displayed on a slate against that particular stack.

2. STEEL
- Steel should be stored diameter wise in a steelyard and should be locked with M.S. chains.
- Access to the steelyard with approach road for vehicles should be provided.
- To avoid rusting. steel should not be directly placed on the ground. Cement blocks should be used as platforms.
- Cut pieces of steel should be stored separately in the steelyard.
- The internal area of the yard should be sufficiently compacted with murum, for easy truck movement.
- Separate space should be provided for columns and beams.
- Sufficient working space should be provided for the fitters.
- Unusable scrap should be stacked in a separate corner until it is disposed of.
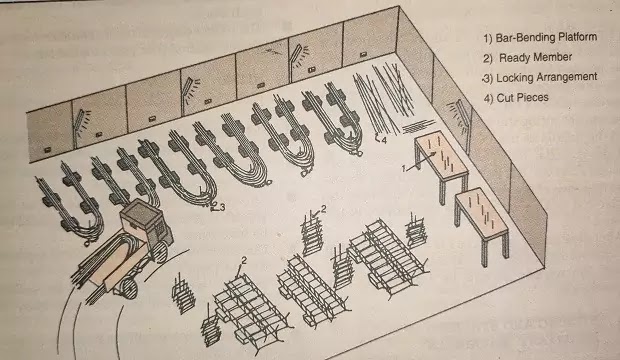 |
| Stell stacking, yard |
- All these materials should be stacked separately.
- Avoid excess lead by unloading the truck at a minimum distance from the workplace.
- Dust and grit should be unloaded near the block-making machine.
- A base surface of shahabad flooring or 7.5 (3″) P.C.C. laid in the leveled surface should be prepared to unload all these materials. to avoid any possible direct contact of materials with the soil.
- Proper access roads should be provided up to the stacking place.
4. BRICKS
- While unloading the truck, bricks should not be thrown.
- They should be stacked systematically, for easy use and counting.
- They should be unloaded on fairly leveled ground.
- Stacking arrangements should be as shown in the figure, to prevent it from collapsing.
- The stacking place should be located so that the debris/scrap thrown from the building does not fall. on the bricks below.

5. CONCRETE BLOCKS
- Fresh concrete blocks should be stored on leveled ground/below parking area/below a covered area.
- More than 6 blocks should not be stacked one over the other in a single column.
- There should be a minimum of 5cm. the gap between two rows. After every row of 25 blocks, there should be discontinuation.
- This gap helps the curing water to reach up to the bottom of each column. It also allows the circulation of air for drying in a uniform manner, up to the last block of each column.
- For curing, date-wise lots of the blocks should be made. Curing should be done five times a day, for a minimum of 15 days. Boards of the manufacturing date should also be displayed on the day’s lot.
- Blocks should be stacked on a flat face for better stability.
- As far as possible, stock and cure the blocks under the covered portion so as to retain the moisture content.
6. LIME SANLA POWDER
- It should be stored on a raised platform approx. 15 cm. to 20 cm. above ground level.
- Roofs and flooring should be waterproof to prevent contact with water.
- It should be placed where it can be locked.
- Minimum openings should be there.
7. FLUSH DOOR SHUTTERS
- Flush door shutters should be placed horizontally over each other.
- The floor should be waterproof.
- Roofs should be leak-proof to prevent rainwater from leaking into the godown.
- Shutters should be stored where they can be locked.
8. DOOR FRAMES
- Door frames should be placed.
- Vertically with at an angle to the wall.
- Space should be free from dampness/leakage.
- Different sizes of door frames should be easily located in the stack.
- The store should be locked.
- Some scrap of M.S. sheets/wooden planks should be placed at the bottom.
- No stack should have more than ten door frames each.
- The coating of black Japan on top and sides and wooden primer coating on the internal surfaces should be applied immediately.
- The stack should be located away from direct sunlight.
- If the stack cannot be locked, at least M.S. chains and locks should be used to secure it.
- Precautionary measures should be taken to ensure that the bottom stay angles and central wooden bracing remain intact.

9. DOOR FITTINGS
- Always store in cupboards, to ensure that the fittings are not affected by dust).
- The store should be free from dampness/ leakage.
- Stack under lock and key.
- Proper stock details should be displayed.
10. PLUMBING MATERIAL
- Racks in the M.S. frame, with horizontal/vertical cardboard sheets/wooden planks, allow the separation of individual fitting as shown in fig.
- Make 2 to 3 racks as per the requirement of the material.
- G.L/P.V.C. pipe should be stored lot-wise (i.e. make, class) (Refer fig. 11.7 (b)).
- Label each compartment with updated stock.

11. C.P. Fittings
- They should be stored under lock and key, preferably in cupboards.
- Item-wise racks should be made for storing the fittings.
- The complete stock should be displayed on each rack of the cupboard.
- Packings of C. P. fittings should be removed before using, to verify brand quality, etc.
12. SANITARY WARES
- These are expensive items and should be stored in a safe place, preferably with locking arrangements.
- Remove the packing before stacking for quality brand testing.
- Heavy materials like G.I. pipe, C.I. Pipe, and fittings should not be stacked along with sanitary ware items, so as to prevent accidental damages.
13. ROLLING SHUTTER ALUMINIUM WINDOW MATERIALS
- The responsibility of stacking these materials lies with the contractor since the order is placed inclusive of material and fixing of rolling shutters.
- This store should have two keys, for the contractor and the storekeeper.
- All the materials like rolling shutters, shaft clips. panel boxes, aluminum boxes, aluminum tracks, etc. should be kept horizontally lengthwise on the ground.
- The store should be properly covered to safeguard it from water and dampness.
14. M.S. GRILL M.S. WINDOW
- Stack vertically at an angle to the wall, to prevent the collapsing of windows.
- Space should be leveled and be free of dampness/leakages. to prevent rusting.
- Always lock all the windows with the M.S. chain.
- Stays/handles will not come along with the lot. They are delivered separately and must be stored in the cupboard itself.
- Locating/removing windows of any size should be easily possible in the stack.
15. WOODEN PLANKS
- Always store horizontally.
- Space should be free from dampness/leakages.
- Throwing it from scaffolding or from a height during work must be prohibited to avoid breakage and wastes.
- Nail cross-wise wooden Chavi, for extra support to a cracked plank.
- Chapatti should be fixed immediately after receipt of the planks, if not provided by the supplier.

16. MOSAIC TILES SKIRTING
- These are stacked on edges at an angle to the wall.
- The store should be free from dampness.
- The floor should be in level.
- Lot wise difference, in stacking, should be maintained.
- It should be stacked under locking arrangements only.
- The stocking period should be minimum. It should be used as soon as it is received on site.
- Different stackings with different color stripes on tiles should be arranged.
- Should be stacked in a covered area. Do not expose directly to sunlight.
17. GLAZED CERAMIC TILES
- The store should be free from dampness.
- The floor should be in level.
- Stacking should be done lot-wise, quality-wise (first, second, etc.), color-wise and size-wise.
- Lot-wise differences in stacking should be maintained for the first and commercial quality, color, size, etc.
- It should be stored under locking arrangements.
- The procedure followed is the same as stone materials such as marble, granite, etc.
HOW TO ISSUE THE MATERIAL FROM STORE
The storekeeper should observe the following pointers while issuing material.
- It should be issued only after receiving the material issue slip from the respective site engineer for the respective building.
- While issuing material from the store, the material should be checked for any damages/wastage must observe the golden rule of first in-out.
- Aný balance material should be collected from the respective persons, making the requisite entries after the day’s work.
- The material should be issued exactly as per the instructions on the material issue slip.
- At the end of the day’s work, all materials are issued a consumption chart.
- This chart should also indicate the day-to-day balance stock of each consumed material, after deduction of the day’s consumption.
- This chart is submitted to P.E by the storekeeper for further reporting to C.E, along with DPR.
DETAILED PROCEDURE FOR ISSUE OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIAL
STEP 1
The contractor his representative will demand the material required for the day’s work. This work is planned and discussed with the engineers the previses day or unpredicted alterations on that day.
STEP 2
The Engineer will issue the material issue slip to the contractor/representative.
- The writing should be legible and neat.
- It should indicate the location of the work and the work details.
- The material that will be consumed should be clearly mentioned.
- Quantity of material required.
- Description of material with details of type, class, etc. should be mentioned.
- The engineer should sign the issue slip.
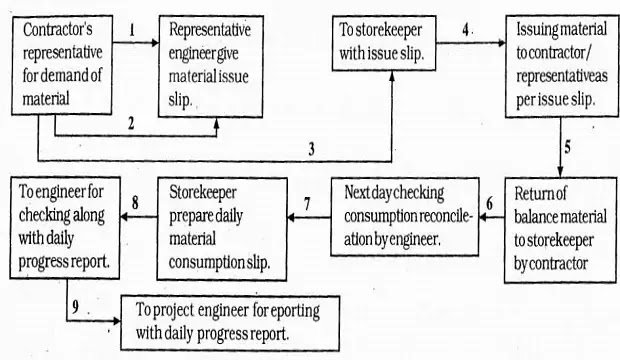 |
| Detail procedure of issue of material |
STEP 3
All materials should be issued strictly under the supervision of the storekeeper.
- The material should be checked before the issue.
- Material that is received first should be issued first.
- The quantity of material should be exactly as shown on the issue slip.
- The contractor/representative should sign the issue slip as acceptance of the material.
- All material issued should be recorded immediately non-consumable materials register.
STEP 4
After the day’s work, the balance material, if any, ould be returned to the stores.
- The storekeeper should visit the workplace during work hours, to see that there is no wastage.
- The entry of any returned material should be made immediately in the consumable/non- consumable register and actual consumption should be noted.
- The contractor representative should sign this register.
STEP 5
The engineer will take the measurements of the work done on the previous day. Reconciliation will be done and the storekeeper’s recording will be cross-checked.
STEP 6
The storekeeper will make entries on the daily material consumption chart, along with the balance stock of consumable items for that particular day.
STEP 7
The engineer will cross-check all consumption recorded and submit the daily material consumption report to the project engineer.
STEP 8
After checking the entries, the project engineer will submit his report along with other daily reports to the chief engineer.
CONTROL POINTS FOR ISSUE OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIAL
The contractor’s work should be carried out as per the instructions and planning of the site engineer. If it is observed that the contractor is not working as specified, the issue of materials can be delayed or stopped. This decision should be taken for the following reasons –
BY BUILDING SITE ENGINEER
- If the contractor does not clean the previous day’s work properly.
- If he delays curing or makes improper arrangements for curing.
- If manpower for repairs of the faulty works Is not arranged on a priority basis.
- If he diverts his labourers to some work other than specified, then the material issue can be stope.
BY BUILDING CONSTRUCTION STOREKEEPER
- If the contractor is wasting the material.
- If he does not return balance material or empty bags, electric focus, lighting wires, etc.
- If he does not stack the scrap steel in the godown properly.
- If he does not return wooden planks, M.S. ghodies, scaffolding material after completion of the work.
- If he does not co-operate in signing memo notes raised against his name.
PERIODICAL STOCK CHECKING
The storekeeper should check the actual physical stock twice a month, For this, he may ask for the site engineer’s help. The stock recorded, should be counter-signed by the project engineer. Any discrepancies found should be communicated to the head office immediately.
Materials should be stored separately for minimizing the time required for stock checking under the following categories.
- Hardware
- Plumbing
- Sanitary ware
- Steel
- Painting
- Electrical
- Miscellaneous
- The storekeeper should clean and rearrange the store periodically. Labeling of Items should be done. Entry in the store during such works should be restricted to the site staff.
- The godowns should be locked and sealed with paper, signed by the watchman and the storekeeper together with the due date, time, and the site stamp every day.
- It should be unlocked on the next working, day, the presence of the storekeeper, engineer, and the watchman on duty.
- The storekeeper should prepare daily material Consumption reports for all consumable he materials and record them in the register daily.
- But materials which are not issued directly by the storekeeper,e, steel, sand, metal, gt, dust, etc, daily consumption report is not possible.
- In this case, the concerned engineer should prepare the consumption statement and give it to the storekeeper on every 14th and 29th of the month for preparing the fortnightly report.
- For timely feedback of material consumption and reconciliation, the engineer should submit the reports in time, The project engineer should deal strictly in this matter, He should instruct the storekeeper to collect the reports from the concerned engineer in time.
- If the considerable difference in actual stock and recorded stock is observed by the project head, then all the recordings should be corrected as per actual stock after thorough checking and verification.
- Also, a written explanation should be submitted by the project head, detailing all the corrected entries in the record.
IMPORTANT NOTE
Keeping the stores updated is very important. Not only storekeepers but the site engineer should also participate actively and effectively in the storekeeping activity. The engineers should also attend to other systems on the site like the safety of temporary electrical wiring, cleaning, wastage control, etc.
The Project Engineer should allot duties in rotation to every engineer, for checking the store daily, as per the given format.
Also, Read This.
Very Good And informative. Please share more on 5S system and storing and stacking of Bulk materials, Consumables, POL, Pherishable Goods.
I need to print this file
ok contol+p press
please share to pdf formate for all details
Good job 👏👏👏👏👏 l am in construction company and you file has helped me to gain a lot of knowledge in all areas you highlights please share how security guard in construction site role and procedures and their relationship with storekeeper and other departments in construction.